You are here
news
Church of San Giorgio in Velabro
Location
Itineraries

Travel Info

Form contatti
[contact-form 5 "Customer Care_EN"]
Credits
ROMA CAPITALE DIPARTIMENTO GRANDI EVENTI, SPORT, TURISMO E MODA
Head of the Department
Patrizia Del Vecchio
Coordination
Francesca Cellamare
Tourism Area Coordinator
Carlo Guarino
Web Manager
Rosario Boccarossa
Social Media Manager
Elisabetta Giuliani
Web Editors
Marina Moretti
Luciana Pelosi
Cristina Ribacchi
Simonetta Salvioni
Social Media Editors
Laura Dal Pont
Pier Paolo Mancuso
Maria Teresa Penserini
Daniele Veroli
IT System Manager
Luca Pavone
Site Creation
Please note: some of the contents of Turismoroma come from the Tourism and Culture database of the city of Rome www.060608.it
Rome for you

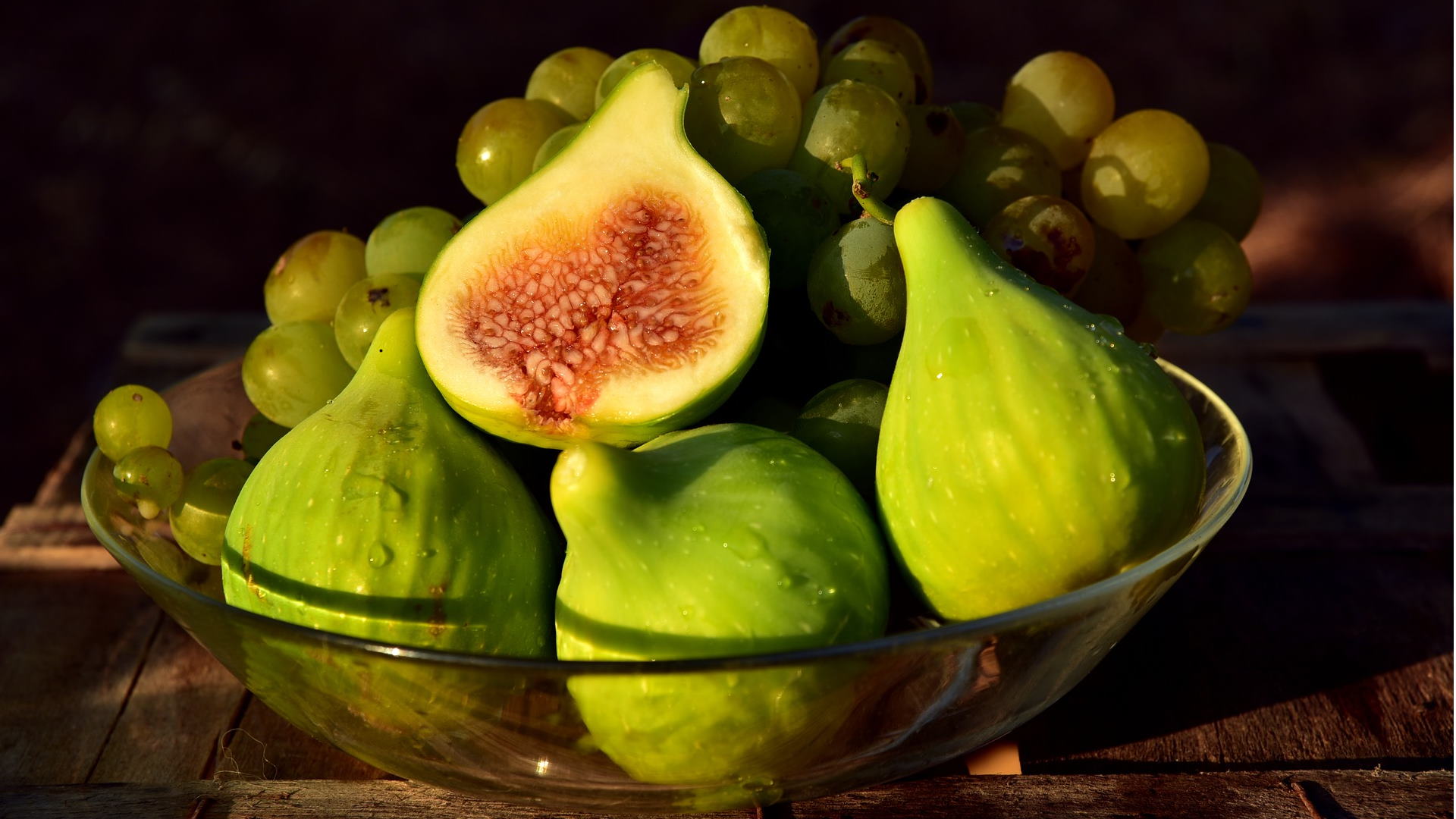
Figs
Che figo! (lit. What a fig!) - So cool!
A first love is never forgotten: the fig is believed to be the oldest cultivated fruit in the Mediterranean area and has left evidence of its importance in art, culture and religion since the dawn of time. Just to give a few examples: in the Old Testament it was synonymous with wealth and abundance, for the ancient Egyptians it was a symbol of the victory over death, ancient Greeks attributed its birth to the god Dionysus and considered its fruits “worthy of nourishing orators and philosophers”. Plato was so fond of figs that he was nicknamed “fig eater” and advised his young students to eat plenty of them because, he said, “they boost intelligence”. In addition to being rich in sugar, they contain high levels of calcium, iron and potassium, phosphorus and vitamins, and have good antioxidant, energizing and anti-inflammatory properties.
A city founded on figs
Their sweetness and virtues did not fail to seduce the ancient Romans who over time spread their cultivation throughout the Italian peninsula and the whole Empire. After all, the fig tree was also connected to the foundation of Rome: legend has it that near a wild fig – the Ficus Ruminalis – the floating trough with Romulus and Remus came to rest and beneath the fig the she-wolf suckled and fed the twins. According to historians, after the demise of the old tree on the Palatine’s slopes another fig sprouted spontaneously in the Forum: the plant was considered a good omen and the fate of the city depended on its state of health, which explains why it was promptly replaced as soon as it dried up... And always under a fig tree the feasts of Juno Caprotina were celebrated on 7 July, an ancient all-female solemnity attended by handmaids and free women.
Fatal figs
Tender and utterly seductive, figs have won hearts but have also started wars: because of them Rome’s historical rival Carthage was destroyed. In the second century BC, “Carthago delenda est”, “Carthage must be destroyed” was the admonition constantly repeated by Marcus Porcius Cato, otherwise known as Cato the Censor, convinced that the Romans should never come to terms with their age-old enemy. Too dangerous and, above all, too close. A proof thereof? A basket of fresh figs coming straight from Carthage, exhibited as a powerful tool of persuasion to all the senators who were reluctant to a military intervention. But figs are also linked to the death of Cleopatra, the Egyptian queen famous in history as the lover of Julius Caesar and later of Marcus Anthony. Cleopatra loved figs so much that she wanted the asp with which she killed herself to be hidden among their leaves. At least according to what Plutarch says... Lastly, rumors had it that Augustus was killed with a poisoned fig that his wife Livia gave him.
In art and cuisine
Today, the varieties of figs run into the hundreds but Pliny already listed 29 of them, including the purple and extra sweet “Black Brogiotto”, the pot-bellied protagonist of many Renaissance still lifes. A basket filled with magnificent ripe green and black figs is shown in a famous fresco from Poppea’s Villa at Oplontis: since ancient times, figs inspired artists and food lovers alike. Suitable for young and old, and, according to Pliny, even able to reduce wrinkles, they accompanied desserts and cheeses, or were flavored with salt, vinegar and garum, a fish sauce. By boiling them, Romans produced the so-called “fig honey”, precious for sweetening food. Ancient recipes also include the special dried fig loin (to be pounded with feet) by Columella and the “iecur ficatum” by Apicius, the most famous gastronome in ancient Rome. This was a delicacy based on the liver of animals fattened with figs, and it was so fashionable that it also influenced the dictionary: not from “iecur” but from “ficatum” comes the word “fegato”, the Italian for “liver”.
How much is a dried fig worth
The fresh fig is a rare commodity that you can only get in the summer and early fall – with a smaller harvest in June, and a larger harvest from July to September. In order to preserve and eat fig fruits throughout the year, people soon learned to dry them: many dried figs have been found, for example, in the Herculaneum archeological site, stored in clay or glass containers. Ovid says dried figs, dates and honey were offered on New Year’s Eve to friends and relatives as a wish for the new year. But the Roman Empire itself was built on figs: Tacitus, in his Annales, explains that legionaries were paid with a handful of salt (hence the name salary) and dried figs, which were very useful in military campaigns since they are so nutrient dense. An old soldier, unable to defend Rome, was “not worth a dried fig”, an expression used still today to indicate someone or something that has no use.
Noble and popular
Emperor Augustus ate them with cheese and fish, Gallienus offered them in his sumptuous banquets but figs, plentiful and easily grown, were appreciated by less well-to-do classes due to their energetic properties, were included in the meals granted to slaves and have been a staple of farmers’ diets for centuries, so much so that they were called the bread of the poor. So, at the time of Emperor Diocletian, the cheapest product on the market was a paste obtained by pounding and mixing with aromatic herbs figs left to dry in the sun. Today, figs color and give flavor to every type of dish and continue to play a leading role, both in gourmet recipes and in simple yet sublime traditional dishes that the Romans still love: pizza and figs or prosciutto and figs.

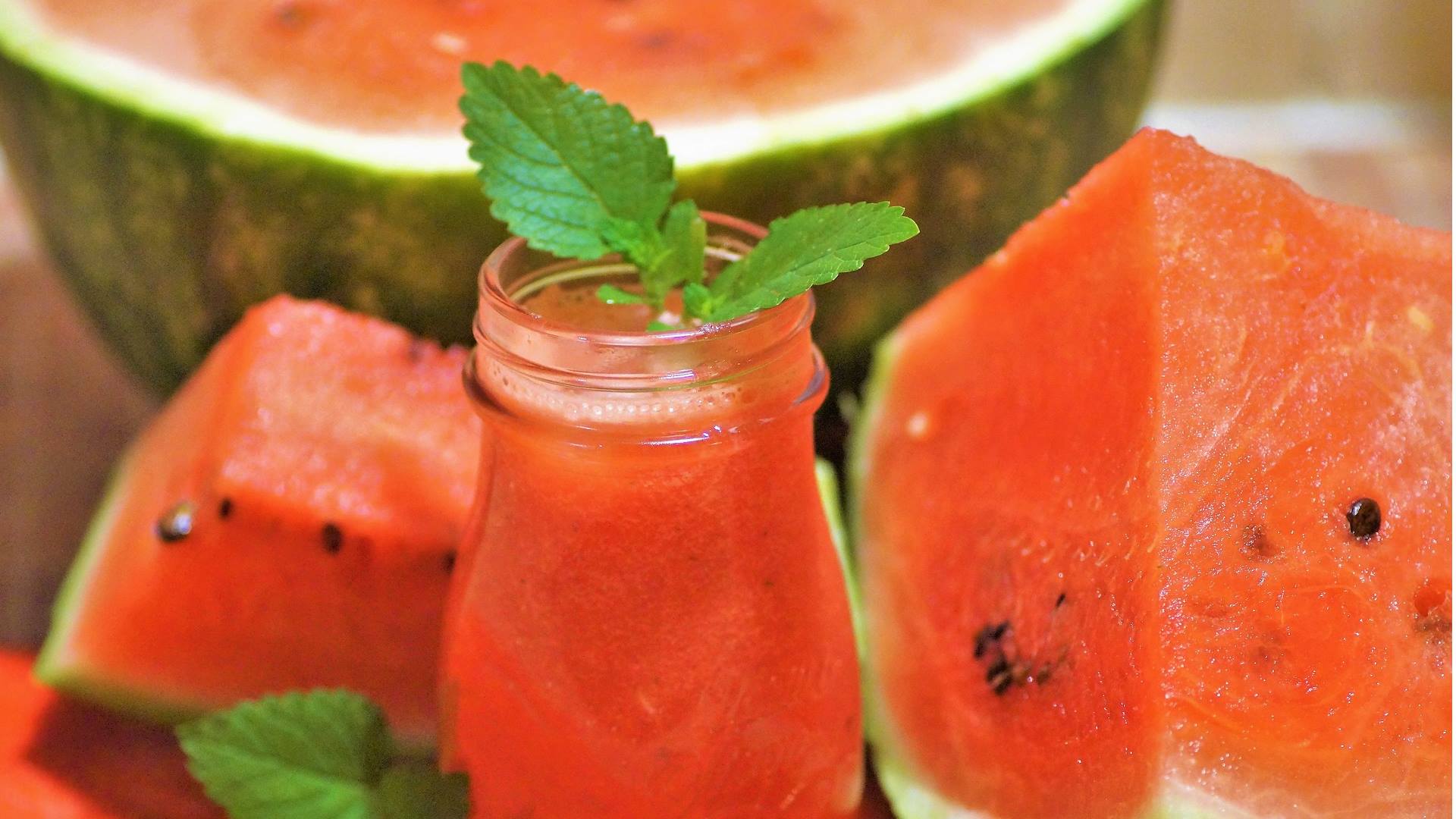
The Summer king of fruits; the cocomero (the watermelon)
The origins
This refreshing and popular fruit has many names. Let’s start with the most appropriate one, which takes up the botanists’ term: "cocomero." It is used all over central Italy and, above all in Rome, akin to the scientific Latin name, Cucumis citrullus. “Anguria” is used throughout northern Italy (and there are many dialect variants). “Anguria” takes us back to the late Greek “angurion”, which actually meant cucumber.
The term derives from the times of Byzantine rule in circa the sixth century AD. From the Exarchate of Ravenna, the use of this term spread throughout northern Italy. In Latin, “cucumis” was not to be found in any form until Virgil used it to indicate the cucumber. We owe use of the term, “cucumis” (indicating the watermelon), to Pliny. The “anguria” version can be traced back to Aetius, a sixth century physician, who used the word “aggourion” to refer to the watermelon. In southern Italy, instead, watermelons are generally known by the name “mellone d’acqua” or “melone d’acqua” (literally, watermelon). In Tuscany the term “popone” is also used.
Whether we call it an “anguria” or “cocomero”, this fruit belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family, originating in the Africa of the tropics. Certain historical sources date the first harvests as far back as Ancient Egypt, nearly 5,000 years ago. The presence of watermelons has been recorded in a number of hieroglyphs. This fruit was frequently placed in the tombs of the pharaohs as a form of sustenance in the hereafter.
The fruit of tradition
According to Roman traditions, the “cocomero” is unmissable on the table at the end of the lunch on 15 August, the feast day of "Ferragosto", when simple home-cooked dishes are served up for family get-togethers. Rosa and Roberta D’Ancona, in their “La cucina romana” (Roman cuisine), recommend prosciutto and iced melon for starters, then an egg pasta dish (“fettuccine all’uovo” or "lasagne" with meat sauce), traditional Roman-style chicken or chicken pieces with peppers, and a mixed loose-leaf lettuce salad, followed by the fresh and tasty “cocomero”. No table can be without it on such a day! Even nowadays, on 15 August, you can hear the sellers of sliced watermelons saying “taja ch’è rosso” (“cut it; it’s red”). The watermelon is, indeed, an extraordinary fruit. There are about 50 species, and we can find them on the marketplace stalls until September. Thanks to the quality of the soil, the watermelons grown in the Agro Romano farmlands nearby Rome (and in particular in Maccarese and Torre in Pietra) are especially delicious.
How can you tell the watermelon’s ripe and ready to eat?
The first thing you must do when buying a watermelon is to check if it’s ripe. There are two approaches. First, look at the skin. It must be firm and tight. If scratched with your fingernail it detaches itself easily. Second, tap the watermelons with your knuckles. If the sound is clear and distinct, the watermelon is of a good quality, ripe and full of water. When you split it open, the pulp must be firm but juicy, bright red and with no white striping or spots.
A slice of watermelon
You may not think so, but it’s a serious business. If you want to save a slice of your watermelon and fully conserve its taste and texture, you have to follow certain rules. Watermelons stored at ambient temperature are more nutritious than watermelons from the fridge or just harvested. You should place your watermelon in the fridge minutes before serving it, and it must be consumed on the same day. Watermelons are excellent on their own, sliced or diced, as an ingredient for fruit salads, jams and “granita” crushed ice drinks, or served with ice cream (the pulp makes an excellent sorbet or sherbet).
Recipe: Watermelon sorbet
Ingredients:
- Watermelon, 600 g of the pulp
- The white of 1 egg
- Sugar 130 g
- Water, 260 gr
Instructions
Cut the watermelon in half, then slice it. Remove the skin and then remove all the seeds from 600 g of the pulp. With a mixer, liquidise the pulp and pour into a bowl. Prepare the sugar syrup: heat a pan with 270 g of water, add the sugar and allow it to fully dissolve until the water boils. Turn off the flame after 5 minutes, pour this syrup into a bowl and leave to cool to ambient temperature. Place the watermelon pulp and the syrup in the fridge for at least 30 minutes to cool thoroughly. Then squeeze a lemon and filter the juice off to remove the seeds. Add the syrup and lemon juice to the pulp. Now whip the white of the egg. Then, using a whisk, mix it into the watermelon thoroughly. The mixture must be smooth. Pour the cool mixture into an ice cream machine and leave to thicken until you obtain a creamy sorbet (20-30 minutes). If you have no ice cream machine, place the mixture in your freezer. Remember that, for a creamy consistency, you must stir occasionally with a fork. Serve your watermelon sorbet cold. Consume it immediately.

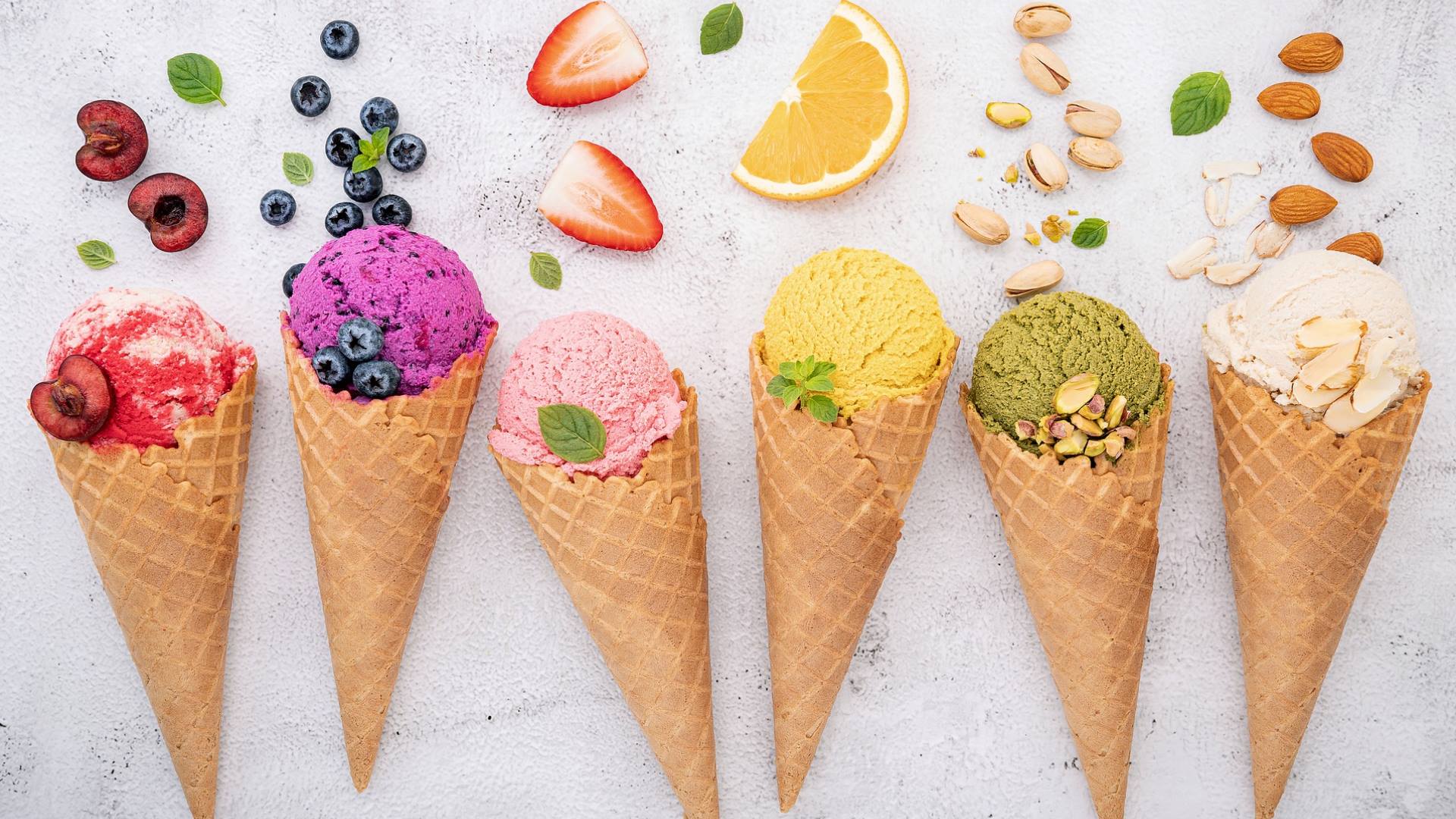
Artisan gelato
Artisan gelato, a fascinating history of the fusion of cultures.
The tradition
From the Egyptians to the recipes of Pliny the Elder, to the “walk and eat ice cream” of today, the history of ice cream and sorbet is fascinating and much more complex than you might think. The evidence points to an ancient tradition that traces its roots as far back as the 12th millennium BC when people began to appreciate the benefits of a “cold drink” and preserve fruit, milk and honey, the only sweetener known of at least until the end of the 9th century.
It was during this period, when the Arabs conquered Sicily, that the use of sugar cane began to spread and meet with the flavours of the Mediterranean and the ice caves of Mount Etna known as neviere, to create the first sorbets. During the Middle Ages a technique was developed in Asia that became known in different regions of the Italian peninsula, of freezing juices by placing them in containers surrounded by ice.
However, it was not until the Renaissance that ice cream and sorbet featured in the banquets of courts and sovereigns to bring prestige to eminent families, in monasteries for their illustrious guests, and in the recipe books of cookery scholars. On marrying the future King of France in 1533, Catherine de’ Medici took with her Ruggeri, an ingenious poulterer, for his phenomenal invention of “sweet and perfumed water ice”, which bewitched the palates of the court. Similarly, in the second half of the 16th century the brilliant and eclectic architect Bernardo Buontalenti installed special ice houses in Florence to introduce frozen flavours to court banquets.
Indeed “iced water” appears in a royal patent by Louis XIV of France for Procopio de’ Coltelli from Messina, founder of the famous Caffè Procope, who is credited with introducing ice creams, granitas and sorbets to France at the end of the 17th century.
The profession of ice cream chef soon emerged in the 16th and 17th centuries, with great chefs constantly perfecting the technique and contributing to its rise and global spread in the 19th and 20th centuries. Several incredible recipes have been discovered in the past, such as bread ice cream dating from the late 18th century, and a recipe from 1808 by Francesco Leonardi for truffle ice cream. A rich history of the exchange of cultural influences between people.
But how does artisan gelato differ from industrial gelato? To understand more we compare the two types. Artisan gelato is characterized by the use of fresh raw materials in season, it contains less fat and less air than industrial gelato, and is served at a higher temperature. This means it has more flavour on contact with the tongue and less calories to burn ‒ around 1/3 compared to industrial gelato! Why not try making gelato at home? With or without an ice cream maker, but with fruit strictly in season!
Recipe: Fruit Gelato
Ingredients
1/2 milk Vanilla pod
4 egg yolks
6 spoons of sugar
150g of fruit
Method
Pour the milk into a pan, add the vanilla pod and bring to the boil over a very low heat. Take the four egg yolks and add them to the sugar, whipping it until pale and fluffy. Add this mixture to the sieved milk and heat until it thickens. Add the 150 grams of fruit that has been puréed, and pour the mixture into a steel mould. Leave to rest in the freezer until solid and stir with a spatula before serving.
Where to eat it
Rome offers excellent artisan gelato shops. To spot them, look at the colours of the gelato and whether the flavours available are in season or not.